How to open ports 80 and 43 in FirewallD
FirewallD is the default firewall management tool for RHEL 7 and Centos 7 systems. Let's learn how to open ports 80 and 43 in FirewallID in this article.
04/09/2025

Đang Tải...
This article provides step-by-step instructions on using the command-line tools Ping and Traceroute, which are simple and easy ways to check network connectivity.
Mục lục
Mục lục
Ping and tracert are commands used to check network connectivity.
Ping is a command-line tool used to check network connectivity between your computer and another server or IP address. Your computer sends ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets to the destination address and waits for a response.
Tracert (also known as traceroute or tracepath) is used to trace and display the route taken by packets from your computer to another server or IP address. This command helps identify intermediate routers through which packets pass before reaching the destination.
Access Start -> Run or use the Windows + R key combination, type cmd and press Ok.
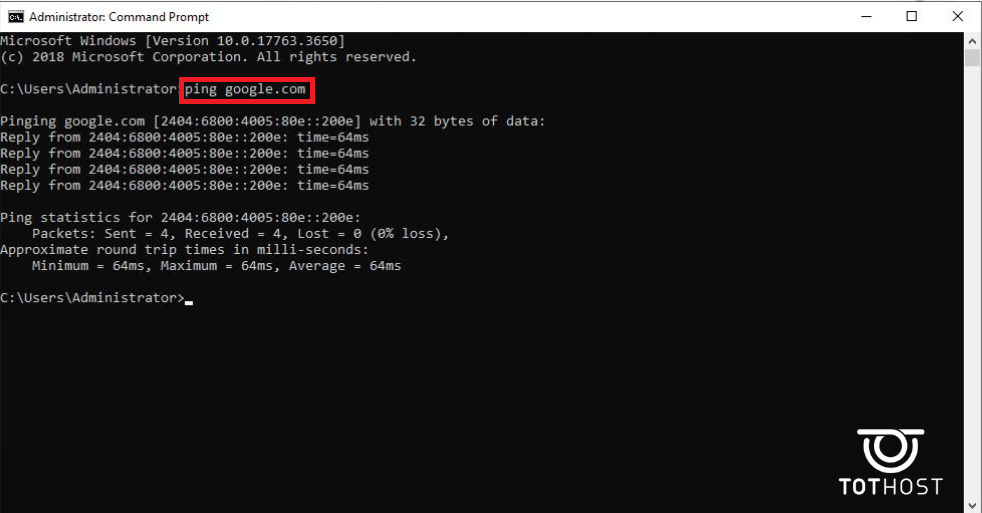
To ping a website, use the syntax "ping + website". For example: ping google.com
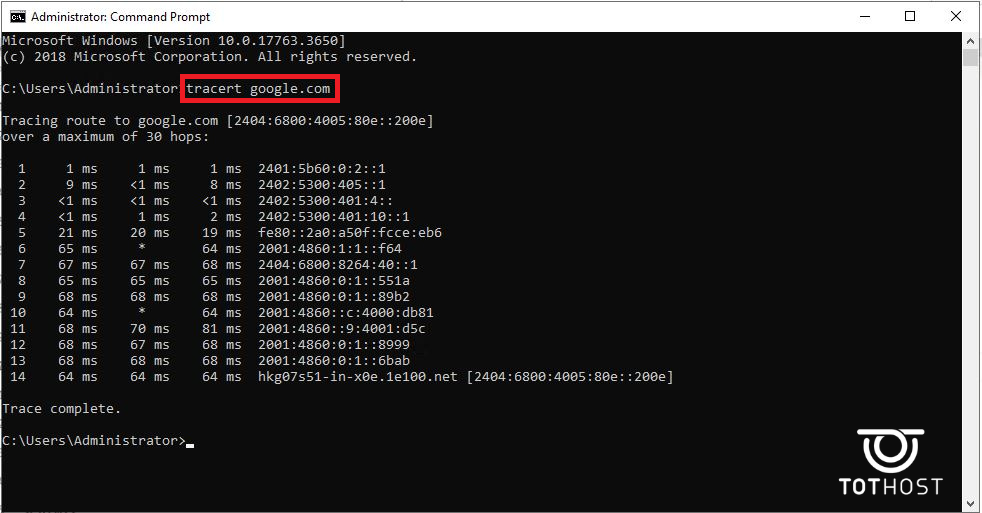
Similarly, to trace the route to a website, use "tracert + website". For example: tracert google.com
On MacOS, access Terminal using the Command (⌘) + Space key combination, then type "Terminal". Alternatively, you can use Siri to search for and open Terminal. Use the ping and traceroute syntax as in Windows.
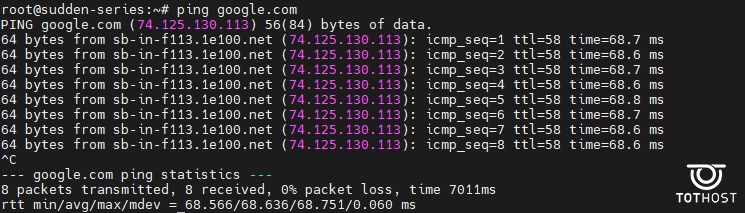
For Linux, log in via SSH or Putty, then use the ping command to check the website you want. If you are unsure how to log in to a Linux server, refer to the article "Guide to: remote & login VPS on Computer".
The ping command will run continuously; to stop it, use the Ctrl + C key combination.
Note: If traceroute is not installed on your OS, install it first using the following command:
Ubuntu/Debian: apt-get install traceroute
CentOS/RHEL: yum install traceroute
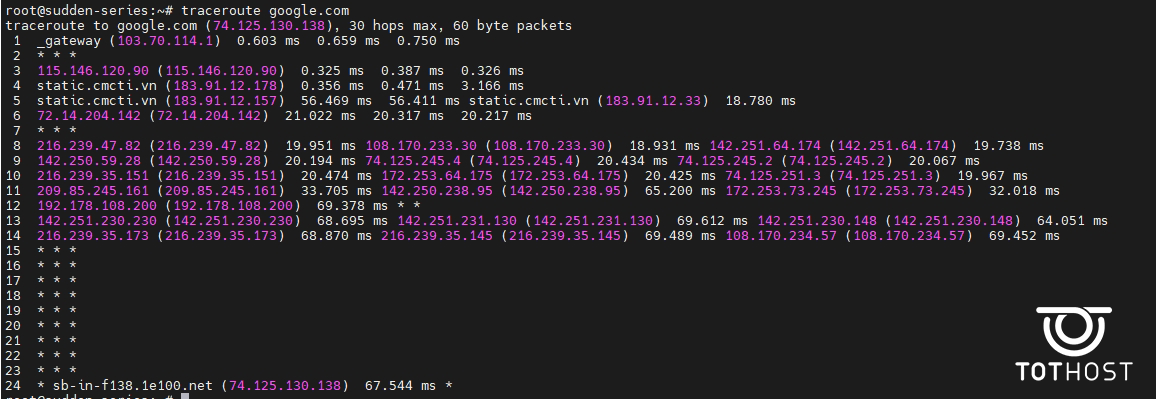
The tracert command on Linux is replaced with traceroute or tracepath: "traceroute google.com"
IP address after "Reply from:" indicates the responding machine. bytes=32: size of the packet sent. time=23ms: round-trip time. TTL=118: Time to Live value of the packet; if it expires, the packet is discarded (maximum TTL is 225).
Additionally, if the results show "*", or "Request timed out", there are connectivity issues that need to be resolved.